Network Segmentation: Mastering Digital Defenses Best Practices in 2024
So, what exactly is Network Segmentation, you ask? Well, in simple terms, it’s the process of dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated segments or subnets. It’s like having different rooms in your house for different purposes – you wouldn’t want your kids’ playroom to be right next to your home office, would you?
“Network segmentation is like having a well-organized wardrobe – you can easily find what you need without digging through a mess of tangled wires and cables.”
Now, let’s dive into the best practices that’ll help you master this crucial aspect of network management.
Network Segmentation Best Practices
In today’s world, where cyber threats lurk around every digital corner, implementing network segmentation best practices is crucial for safeguarding your data and ensuring smooth operations. By dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments, you can contain potential breaches, enhance security, and optimize performance. Let me break it down for you.
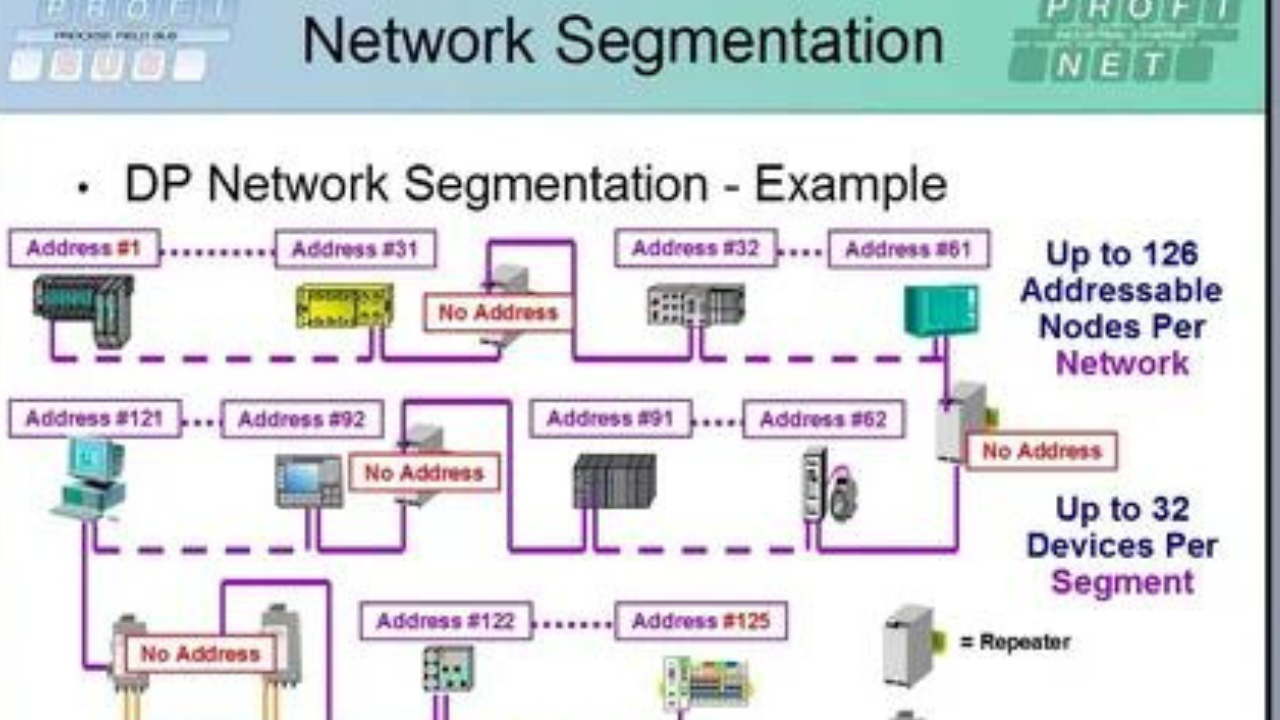
Identify and Isolate Critical Assets: The first step is to identify your most sensitive data, applications, and systems. These are the crown jewels that require the highest level of protection. Isolate them onto dedicated subnets or virtual LANs (VLANs) to minimize exposure and reduce the attack surface.
“Think of it like having a vault within your house for your most prized possessions – you wouldn’t want them out in the open, would you?”
Implement Least Privilege Access: One of the cardinal rules of network security is to grant access only to those who truly need it. By segmenting your network and implementing strict access controls, you can ensure that users and devices can only access the resources they require for their specific roles and responsibilities. This principle of least privilege minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
“It’s like having different keys for different rooms in your house – you wouldn’t give the same key to everyone, right?”
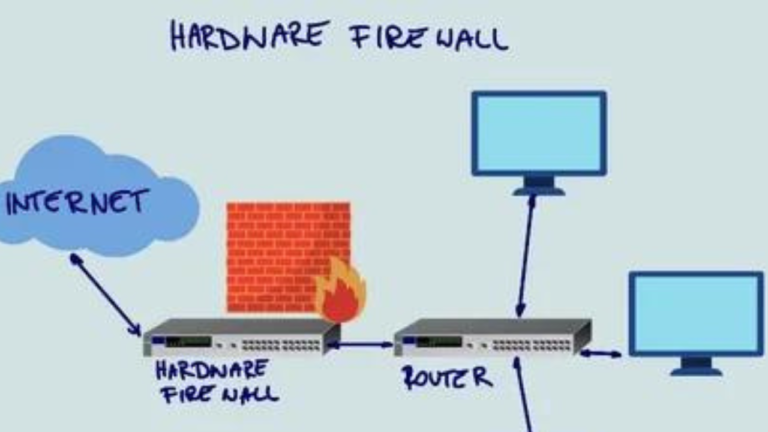
Enforce Firewall Rules: Firewalls are the gatekeepers of your network, and properly configured firewall rules are essential for effective segmentation. Set up rules that restrict traffic between subnets, allowing only authorized communications to pass through. This way, if one segment is compromised, the breach is contained and cannot spread to other parts of the network.
“Imagine each subnet as a separate room with a locked door – the firewall rules determine who can enter and exit each room, keeping the whole house secure.”
Leverage Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs): VLANs are a powerful tool for segmenting your network without the need for physical rewiring. By logically dividing a single physical network into multiple virtual networks, you can isolate different groups, departments, or types of traffic for better security and performance.
“Think of VLANs as invisible walls within your house, separating different areas without having to tear down and rebuild actual walls.”
Monitor and Log Network Activity: Segmentation alone is not enough – you need to actively monitor and log network activity to detect and respond to potential threats. Implement robust monitoring and logging solutions that can track traffic between segments, alert you to suspicious behavior, and provide valuable forensic data in case of a security incident.
“It’s like having security cameras in your house – you can keep an eye on what’s happening and review the footage if something goes wrong.”
Network Segmentation Best Practices
Why is Network Segmentation important?
Network segmentation is crucial for several reasons:
- Enhanced Security: By dividing your network into isolated segments, you can contain potential threats and prevent them from spreading across the entire network. This minimizes the impact of a security breach and makes it easier to identify and mitigate the affected areas.
- Improved Performance: Segmentation allows you to allocate network resources more efficiently by separating high-traffic applications or user groups onto dedicated subnets. This prevents congestion and ensures optimal performance for critical applications and services.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industry regulations, such as PCI DSS for payment card data and HIPAA for healthcare information, mandate network segmentation to protect sensitive data. Proper segmentation helps organizations meet these compliance requirements and avoid hefty fines or legal repercussions.
- Easier Management: With a segmented network, you can apply specific security policies, access controls, and configurations to different segments based on their unique requirements. This simplifies network management and reduces the risk of misconfigurations or oversights.
How do I determine the appropriate level of Network Segmentation?
Determining the appropriate level of network segmentation depends on several factors, including:
- Size and Complexity of the Network: Larger and more complex networks may require more granular segmentation to effectively manage and secure different components.
- Data Sensitivity: Highly sensitive data, such as financial records, intellectual property, or personal information, should be isolated on separate subnets with stringent access controls.
- Business Requirements: Different departments, applications, or user groups may have varying security and performance requirements, necessitating separate network segments.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify critical assets, potential threats, and the associated risks. This will help you determine the appropriate level of segmentation needed to mitigate those risks.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Certain industries or regulatory bodies may have specific guidelines or mandates for network segmentation that must be adhered to.
It’s essential to strike a balance between security and operational efficiency. Too little segmentation can leave your network vulnerable, while excessive segmentation can lead to management complexities and potential performance issues.
What are the challenges of implementing Network Segmentation?
While network segmentation is a crucial security measure, it does come with its own set of challenges:
- Complexity: Dividing a network into multiple segments can introduce additional complexity in terms of network design, configuration, and management. Proper planning and documentation are essential to avoid errors or oversights.
- Performance Impact: Segmentation can potentially impact network performance if not implemented correctly. For example, if traffic between segments is not optimized or if there are bottlenecks at the intersection points, it can lead to latency and throughput issues.
- Migration and Integration Challenges: Implementing segmentation in an existing network can be challenging, as it may require migrating applications, servers, and devices to new subnets. Integrating segmentation with existing systems and processes can also be a hurdle.
- Access Management: Maintaining proper access controls and user permissions across multiple network segments can become increasingly complex, especially in large environments.
- Cost and Resources: Depending on the segmentation approach (e.g., hardware-based or software-defined), there may be additional costs associated with procuring and maintaining the necessary infrastructure and resources.
Addressing these challenges requires careful planning, robust documentation, and ongoing monitoring and maintenance to ensure that the segmentation implementation remains effective and efficient over time.
What are the different methods of network segmentation?
There are several methods you can use to segment your network, each with its own advantages and considerations:
- Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs): VLANs are a commonly used method that logically divides a single physical network into multiple virtual networks. They are relatively easy to implement and manage, but they may not provide the same level of isolation as physical segmentation.
- Firewalls and Access Control Lists (ACLs): Firewalls and ACLs can be used to restrict traffic between different network segments based on predefined rules. This approach offers granular control but can become complex to manage as the number of rules and segments increases.
- Network Access Control (NAC): NAC solutions enforce access policies based on the user, device, and application attempting to access the network. This method can be effective for controlling access to specific network segments, but it requires additional infrastructure and management overhead.
- Software-Defined Networking (SDN): SDN decouples the control plane from the data plane, allowing for more flexible and programmable network segmentation. This approach offers greater agility and centralized management but may require specialized skills and infrastructure.
- Microsegmentation: Microsegmentation extends segmentation principles down to the individual workload or application level, providing granular isolation and security. This method is particularly useful in virtualized and cloud environments but can be complex to implement and manage.
The choice of segmentation method(s) depends on factors such as your existing infrastructure, security requirements, scalability needs, and available resources. In many cases, a combination of different methods may be necessary to achieve the desired level of network segmentation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is network segmentation necessary for small businesses?
Yes, network segmentation is important for businesses of all sizes



Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.